The Lachman Test is performed by the clinician to assess laxity of the anterior cruciate ligament when there is a suspected tear.
 Page updated March 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
Page updated March 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
What does the Lachman test measure?
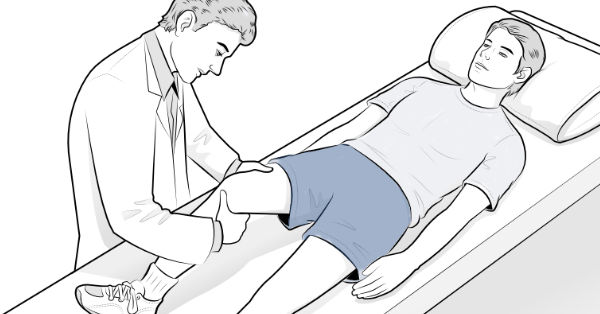
How is the Lachman test performed?
With the patient lying on their back and the head supported, the knee is flexed to 20-30 degrees, and the patient encouraged to totally relax. One hand grasps the femur, while the other grasps the upper tibia with the fingers at the back of the tibia and the thumb in front. Attempt is made to displace the tibia in relation to the femur, feeling both for the degree of displacement and the firmness of the end point.
Grading of the Lachman test
The surgeon will grade the test to allow accurate notes and also changes over time. This is of course rather subjective.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"Grading of ACL laxity is described as 1 through 3, which correlates to mild, moderate, and severe ACL injuries. Mild (grade I) is 0 to 5 mm, moderate is 6 to 10 mm (grade II), and severe is 11 to 15 mm (grade III) of anterior tibial translation compared to the uninjured side."
Citation: Coffey R, Bordoni B. Lachman Test. [Updated 2023 Jul 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554415/
How accurate is the Lachman test?
The Lachman test is not the most accurate of the manual tests for an anterior cruciate ligament tear. If there is blood in the knee, the test may be painful and trigger hamstrings spasm.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
....diagnostic accuracy values for the Lachman test are lower than previously reported" and "...MRI and arthrometry...are recommended when the history is suggestive of an ACL tear, but tests are negative".
Citation: Sokal PA, Norris R, Maddox TW, Oldershaw RA. The diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for anterior cruciate ligament tears are comparable but the Lachman test has been previously overestimated: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022 Oct;30(10):3287-3303. doi: 10.1007/s00167-022-06898-4. Epub 2022 Feb 12. PMID: 35150292; PMCID: PMC9464183.
Other tests include -
Forum discussions
- "The Lachman test"
Patients share their experiences of having tests for cruciate ligament tear.
- ACL Surgery "Not Needed" ?
It can be challenging to decide on ACL reconstruction...