Cartilage fibrillation is an advanced stage of articular cartilage damage, when the normally resilient material breaks down in feathery strands revealing the underneath bone.
 Page updated April 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
Page updated April 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
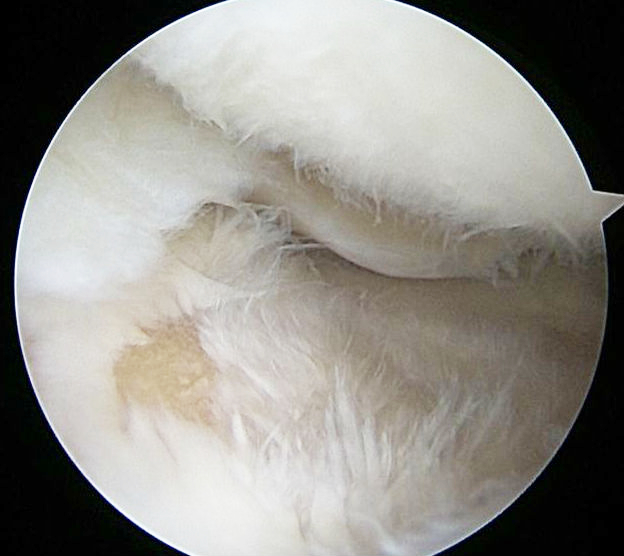
Fibrillar wear of the articular cartilage. You can see the yellowish bone showing on the top of the tibia.
What causes cartilage fibrillation?
In normal joint cartilage the cells or chondrocytes are few and far between, and appear 'suspended' in their background matrix.
In osteoarthritis, however, complex chemical changes wake the chondrocytes up from their apparent dormancy, and a cascade of chemical events creates 'a soup' of inflammatory chemicals and a disruption of the normally quiescent components of the matrix, and disruption of the fibrils within it.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"....The composition and cellular organization of healthy human adult articular cartilage (left panel) is more complex than it looks....[Breakdown of cartilage is due] either to the adverse effects of trauma or overloading (e.g., injury and obesity) on otherwise normal cartilage or normal loading on abnormal cartilage (e.g., genetic defects and aging)...."
Citation: Goldring MB. Articular cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis. HSS J. 2012 Feb;8(1):7-9. doi: 10.1007/s11420-011-9250-z. Epub 2012 Jan 24. PMID: 23372517; PMCID: PMC3295961.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"Cartilage alterations in [osteoarthritis] mainly concern an imbalance in tissue remodeling due to changes in [cartilage cell] behaviour...."
Citation: Roseti L, Desando G, Cavallo C, Petretta M, Grigolo B. Articular Cartilage Regeneration in Osteoarthritis. Cells. 2019 Oct 23;8(11):1305. doi: 10.3390/cells8111305. PMID: 31652798; PMCID: PMC6912428.
Is cartilage fibrillation reversible?
As joint cartilage does not have blood vessels, lymphatics or nerves, its capacity to heal itself once the structure has broken down is limited.
If stem cells are encouraged to enter the area (eg via a microfracture procedure) then some healing may occur, although the quality of cartilage may not be as good as the original.
Most modern cartilage repair procedures involve growing new 'cartilage tissue' in a laboratory and transplanting it back into the defect, where microfracture may have prepared the recipient area for stem cells to also migrate into the area.
How is cartilage damage classified?
The surgeon will generally use an established classification system to note and monitor the extent of any of cartilage damage.