HTO is an abbreviation of 'high tibial osteotomy', a procedure to cut and realign the upper end of the tibia bone to improve lower limb alignment.
 Page updated February 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
Page updated February 2024 by Dr Sheila Strover (Clinical Editor)
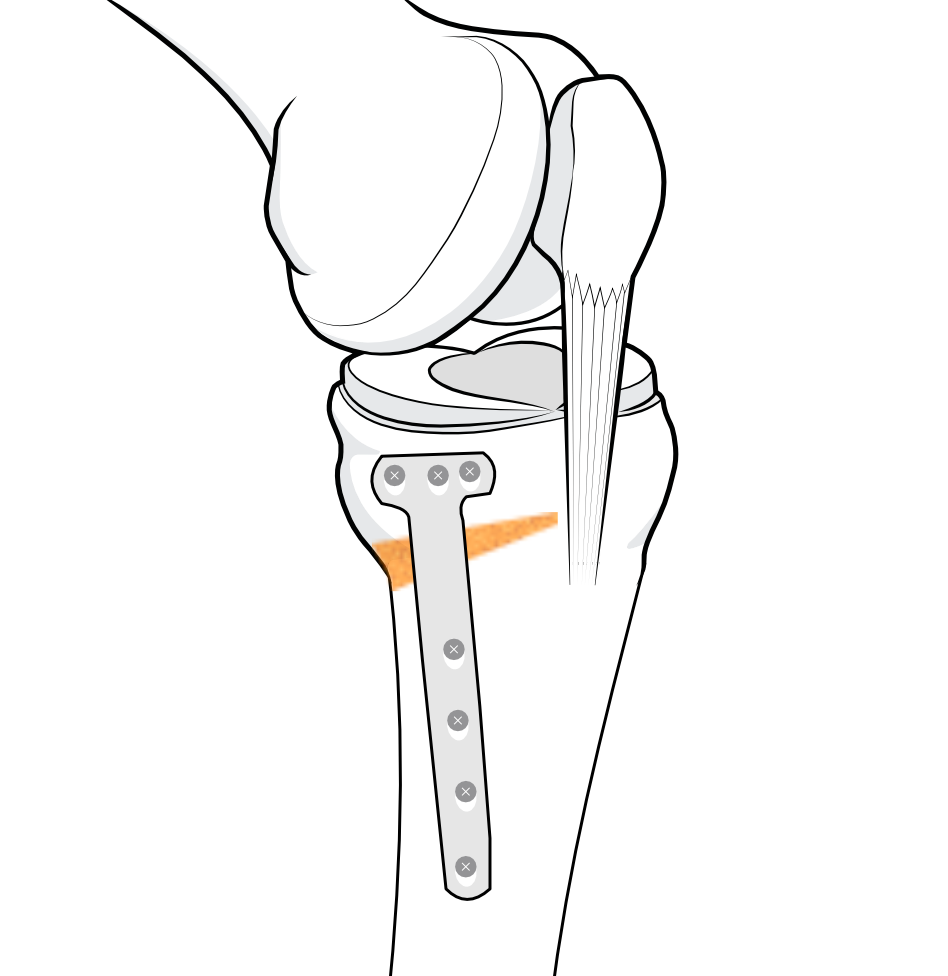
Plate in place and secured with screws.
Why is HTO performed?
HTO or high tibial osteotomy is performed when one side of the knee joint is damaged, but the other side is still healthy, when the surgeon changes the limb alignment to take the person's weight off the damaged side.
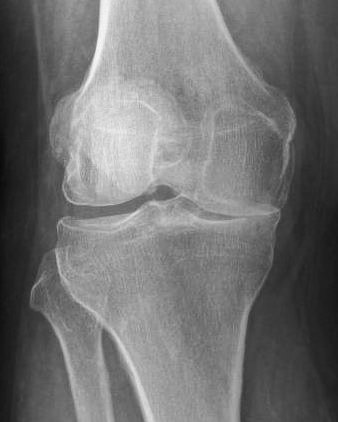
The damage may be from a previous meniscectomy on one side, for example, with early painful arthritis and joint cartilage wear due to lack of shock absorption on that side.
X-ray will show joint space narrowing on one side.
This offloading is possible because there are two main contact points between femur and tibia - the medial and the lateral compartment - and this procedure can shift the forces from the one contact point to the other so that pain from one-sided damage can be relieved.
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
..."with careful planning and execution, osteotomies....allow for return to work and sporting activities without limiting future....[knee replacement]....procedures."
Citation: Murray R, Winkler PW, Shaikh HS, Musahl V. High Tibial Osteotomy for Varus Deformity of the Knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2021 Jul 9;5(7):e21.00141. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-21-00141. PMID: 34242204; PMCID: PMC8274793.
Opening wedge versus closing wedge
Special planning X-rays are done in the days before the final surgery.
From the planning X-rays surgeon will determine what degree of new angulation is required, and whether this can be achieved by opening a gap and allowing new bone to fill the space ('opening-wedge' HTO) or by removing a wedge and fixing the two bony edges together and allowing them to unite ('closing-wedge' HTO).
-
Quote from peer-reviewed paper:
"Opening wedge HTO...does not require a fibular osteotomy, common peroneal nerve dissection, disruption of proximal tibiofibular joint, and bone stock loss as opposed to closing wedge HTO. In addition, opening wedge HTO allows for multiplanar correction and easier subsequent total knee replacement (TKR)....Disadvantages associated with medial opening wedge HTO include the need of bone graft and the risk of nonunion, collapse, or loss of correction."
Citation: Bonasia DE, Governale G, Spolaore S, Rossi R, Amendola A. High tibial osteotomy. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2014 Dec;7(4):292-301. doi: 10.1007/s12178-014-9234-y. PMID: 25129702; PMCID: PMC4596221.
What are the steps of HTO surgery?
In an opening wedge high tibial osteotomy the upper tibia bone is cut almost through and the bone wedged into the altered alignment and fixed in place with a plate and screws until the bone heals.
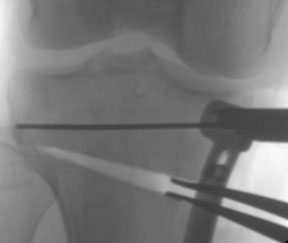
An X-ray is taken during surgery to show the amount to which the laminar spreaders have opened up the wedge before the plate is fixed in place to hold it open.
The value of HTO
Unlike a knee replacement, high tibial osteotomy does not involve the actual joint surfaces themselves. This means that the patient may enjoy several more years of relative comfort before perhaps needing to proceed with a knee replacement.
As the HTO did not interfere with the joint surfaces the knee replacement should be straightforward.
Forum discussions
- High tibial osteotomy
A short discussion between symptomatic patients concerned about bone plate removal.
- High Tibial Osteotomy + Meniscus Transplant - Complete Fracture!
Discussion about the choice of a high tibial osteotomy to decrease the forces on a new meniscus transplant.
Relevant material -
- High tibial osteotomy
- Osteotomy
- Varus
- Limb alignment
- Compartment
- Double-level osteotomy
- Bilateral osteotomy
 2010 - Osteotomy as an adjunct procedure to biologic knee replacement - by Dr Kevin Robert Stone (Knee Surgeon)
2010 - Osteotomy as an adjunct procedure to biologic knee replacement - by Dr Kevin Robert Stone (Knee Surgeon)
 2010 -
2010 -